Social Security Milestones

- Age 62 is the minimum age at which anyone can draw from their Social Security retirement account, though many sometimes confuse it with 59 1/2, which is the minimum age an individual may tap into many IRAs and retirement accounts without penalty.
- Age 65, 66 or 67, depending on your birth date, is the age at which a person can claim full retirement benefit amounts.
- Age 70 is the maximum age for purposes of estimating Social Security benefits.
Full Retirement

Full retirement age, also known as “normal retirement age” had been 65 for many years. However, beginning with people born in 1938 or later, that age gradually increases until it reaches 67 for people born after 1959. Due to so many baby boomers reaching full retirement age, as well as other financial issues plaguing our government, there have been discussions to increase the full retirement age past 67 years old.
The Las Vegas Factor

Social Security is a safety net for many families whose spouse dies suddenly or becomes disabled. It is also the place where you apply for Medicare at the age of 65, regardless of one’s retirement age. An adult child may want to review their parents’ statements to insure its accuracy, especially if their parents are unable to do so.
Page two of an individual’s Social Security statement provides taxpayers with “Your Estimated Benefits.”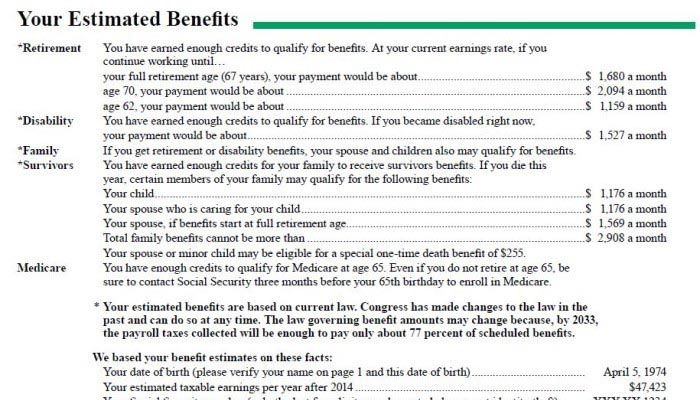
For this exercise, the statement may look something like this:
- At age 62, your payment would be about $880 a month.
- If work until age 66, your payment would be about $1,180 a month.
- If you work to age 70, your payment would be about $1,564 a month.
The calculations provided by SAA are estimates only and are based on elaborate calculations that include assumptions that an individual will continue to earn about the same annual income made during the last several years, and that their life expectancy will be somewhere around what they expect it to be. The current national average is about 77 years.
If an individual lives to 77 years old, we get the following total payout (“Estimated Benefits”) over the years we draw out, which does not include any interest that could be earned with that money:
- At age 62, your payment would be about $880 a month.
- If you work until age 66, your payment would be about $1,180 a month.
- If you work to age 70, your payment would be about $1,564 a month.
This isn’t a typo. Despite the rather large discrepancy in the monthly benefit estimates, if an individual lives the average lifespan, he/she may be better off retiring earlier especially if that individual thinks he/she can invest the money at a better return than Social Security estimates it will make at the Treasury-bond rate. “Actuarially, the government figures it out so it all works out the same; they’re not trying to push people to take it out early, or to take it out late,” says Michael Boone, CEO and charter financial analyst at M.W. Boone. “There are two issues here: They’re assuming you’re average, and they’re assuming their rate of return. The question you have to ask yourself is: Are you average, and what could you actually do with the money if you got it earlier?”
The Wellness Factor

Health is an important factor to consider when considering the best time to retire. Is an individual physically active, in relatively good shape, no bad habits or life-threatening health problems to speak of? Did everyone in that person’s family live until they were into their 90’s? If so, he/she may want to wait for the larger payoff.
“If you live longer than they expect, you are actually better off, all other things being equal, to wait,” says Boone. “The reason for this is you’re getting a larger dollar amount, but you’re getting it longer than they thought.”
The difference could amount to a windfall over time. If an individual lives to 90, their 20 year monthly benefit of $1,564, retiring at 70, will reap a total payout of $375,360 versus $295,680, if he/she retires at 62. (Note: A 90 year old individual receives 8 more years of retirement benefits at a reduced rate if he/she retires at 62, rather than at 70.)
The Recession Has Lasting Pain

Reasons to start collecting as early as possible include: the recent financially devastating recession, historically small retirement savings (some estimates are as low as $30,000 for people 55 and older), increased taxes at certain levels, and senior lifestyles that are more active and expensive. Most people ages 66 to 70 are no longer working, and many are struggling to pay for necessities such as health care. Additionally, fixed income rates on savings are as low as they have been in 60 years with little prospects for significant change in the near future.
Calculators

The Social Security Administration (SSA) has a number of calculators available to determine an individual’s benefits. They can all be accessed through this link. Most can be accessed without having to enter personal information, such as a social security number. Determining the best time to start collecting Social Security retirement benefits requires some planning and understanding how the system works. Here are some popular calculators:
*Earnings Test Calculator– Enter a person’s birth date, estimated earnings, and other information to determine the effect on an individual’s retirement earnings
*Retirement Age Calculator– Enter a person’s birth date year and see how much money that individual and their spouse’s benefits will be reduced if they start taking benefits before their full retirement age.
*Thinking about retiring between 62 and full retirement? – See how much an individual’s social security will be reduced, and what are the pros and cons
Age reduction calculator
Keep Working After Full Retirement

While there is a limit how much money a person can earn while receiving social security benefits ($15,720 this year; for every $2 over that amount earned, the government deducts $1), once an individual reaches full retirement age, this rule no longer applies and that individual can earn as much as he/she likes without any penalties. SSA will factor in any deductions and give that individual a credit.
Claim Spousal Benefits

A person may be eligible to receive Social Security benefits based on their spouse’s work history in addition to their own.
The government will pay you your benefits first, but if the benefits that you’re entitled to through your spouse are higher, you’ll receive a combination that equals your spouse’s benefit.
As with your own benefits, the earlier you collect the less you’ll receive. The maximum you can get is up to one-half what they would be eligible for at full retirement.
One strategy for couples to maximize the benefits they receive is for the spouse who has earned a bigger Social Security payout to file for benefits and then suspend them, allowing the other spouse to claim only spousal benefits while the higher earner waits until age 70. In this scenario, the spouse collecting only a spousal benefit can leave their own Social Security untouched, racking up credits for a bigger monthly payout years later. Note: This “file and suspend strategy” will no longer be in effect after April, 2016. The spouse who is going to file and suspend has to been born no later than May 1, 1950, and submit their request to file and suspend on or before April 29, 2016, so Social Security has time to process their application. This reflects the six-month grand-fathering window including in the 2015 Budget.
Divorcee?

Divorcees are eligible for similar benefits if the couple was married at least 10 years. Note that if the divorcee later remarries, he/she generally can not collect benefits on their former spouse’s record unless their later marriage ends.
NOTE: Retirement planning and navigating through the Social Security system can be a complex business. When nearing retirement, sit down with an accountant or personal finance specialist who can help map out how to best proceed.
